Econometrics Tutor for Warwick EC203 EC226
Experienced Econometrics tutors for online and in-person tutoring for Warwick economics courses.

Topics:
Part 1: Introduction
- Causality and the selection problem. Mostly Harmless Econometrics: chapter 1 & 2. Mastering ‘Metrics: chapter 1. Introductory Econometrics, A Modern Approach: chapter 1.
- Inference: random variables, estimators, distributions, hypothesis testing, confidence intervals. First year notes EC122/124. Using Statistics in Economics: chapter1-7. Introductory Econometrics, A Modern Approach: appendix B.
Part 2: Regression Models
- Causality and the conditional independence assumption (CIA). Mastering ‘Metrics: chapter1.
- The simple linear regression model (SLR) – OLS. Introductory Econometrics, A Modern Approach: chapter 2. Mastering ‘Metrics: chapter2. Econometrics by Example: part I. Introductory Econometrics, chapter 1.
- The multiple linear regression model (MLR) – OLS – Restriction Tests – Coefficient Interpretations. Introductory Econometrics, A Modern Approach: chapter 3-4. Mastering ‘Metrics: chapter2. Econometrics by Example: part I. Introductory Econometrics: chapter 2.6/7 and chapter 3.
- Qualitative/dummy variables – Chow Test – LPM. Introductory Econometrics, A Modern Approach: chapter 7. Econometrics by Example: chapter 3. Introductory Econometrics: chapter 5.
- Standard Error Problems. Heteroskedasticity, Multicollinearity & Non-normality in the errors: consequences, tests and solutions. Introductory Econometrics, A Modern Approach: chapter 3,8. Econometrics by Example: chapter 3,5. Introductory Econometrics: chapter 4,5,7
- Model misspecification. Introductory Econometrics, A Modern Approach: chapter 3, 5, 9. Econometrics by Example: chapter 7. Introductory Econometrics: chapter 6, 8.
Part 3: Extensions
- Randomised control trials (RCTs). Mastering ‘Metrics: chapter 1. Mostly Harmless Econometrics: chapter 1.
- Instrumental variables (IV). Introductory Econometrics, A Modern Approach: chapter 15-16. Mastering ‘Metrics: 98. Econometrics by Example: chapter 19. Introductory Econometrics: chapter 8-9. Mostly Harmless Econometrics: chapter 4.
- Panel data methods, including: first differencing (FD) and fixed effects (FE). Introductory Econometrics, A Modern Approach: chapter 13-14. Mastering ‘Metrics: chapter 5. Econometrics by Example: chapter 17.
- Differences in Differences (DiD). Introductory Econometrics: chapter 13. Mostly Harmless Econometrics: chapter 5.
- Regression discontinuity design (RDD). Mostly Harmless Econometrics: chapter 6. Mastering ‘Metrics: chapter 4.
CLRM Assumptions
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com E[\epsilon]=0](https://econtutor.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-4349362b3b8224b163fac02234197893_l3.png) holds whenever there is an intercept, it means the error term is zero, on average.
holds whenever there is an intercept, it means the error term is zero, on average.- No perfect multicollinearity and all Xs must exhibit some variation (MLR)
- *No perfect linear relationship between the Xs
- *The higher the variation in independent variables, the lower the variance of estimators. To increase variation, increase the sample size.
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com E[\epsilon| X_1, X_2, ..., X_k]=0](https://econtutor.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-93aeb624178f92d4e156480a695f3b1d_l3.png) Conditional independence assumption
Conditional independence assumption
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com E[\epsilon| X_1, X_2, ..., X_k]=E[\epsilon] =0](https://econtutor.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-3b795a1edde4a03e617878dff906ec27_l3.png)
- If this holds, there is no selection effect. (observed effect = causal effect)
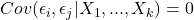 Zero serial correlation in the errors
Zero serial correlation in the errors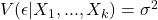 homoskedasticity, or constant conditional variance of the residual term
homoskedasticity, or constant conditional variance of the residual term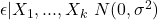 errors are normally distributed with a mean zero and constant variance.
errors are normally distributed with a mean zero and constant variance.
Book a free trial with our Economics Tutor at Warwick University for any economics or finance course.
- EC203 Applied Econometrics Tutor
- EC204 Economics 2
- EC226 Econometrics I
- EC108 Macroeconomics
- EC109 Microeconomics
- EC202 Microeconomics II
- EC201 Macroeconomics II
Other popular courses:
Our tutors are available in Central London, North London, Manchester, Birmingham, Oxford, Bristol, Cambridge, Liverpool, Newcastle, Cardiff, Reading, Durham, Leicester, Lancaster, Sheffield.
